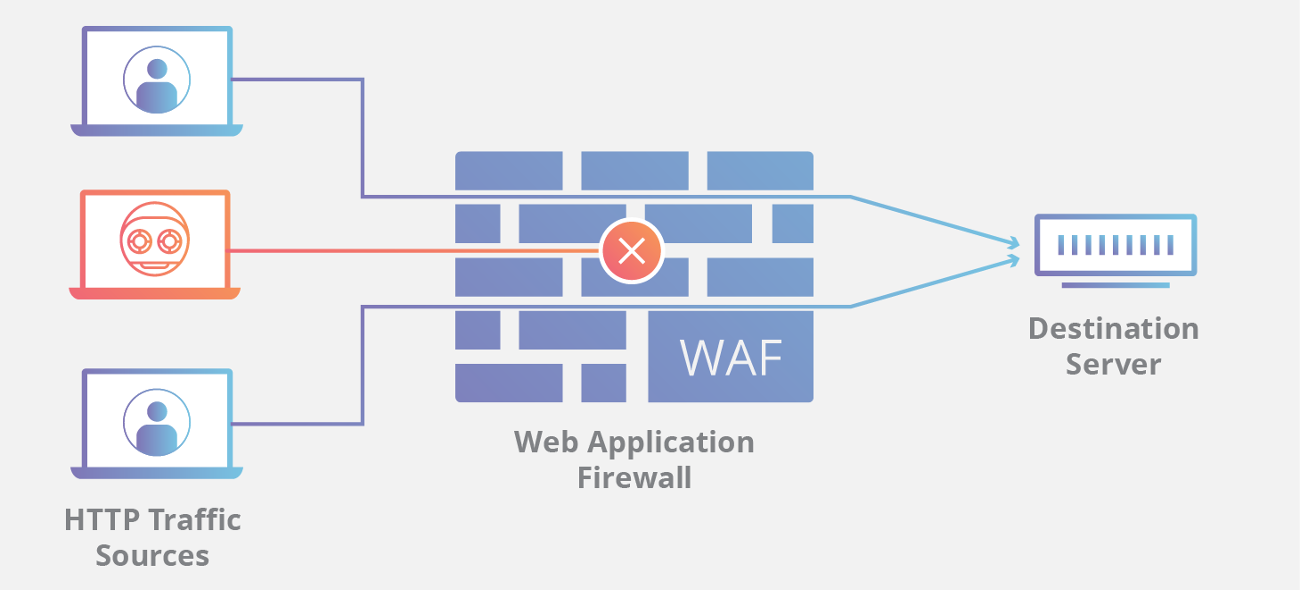
A WAF, or Web Application Firewall, helps in the protection of web applications by filtering and tracking HTTP traffic between the web application and the Internet. It normally protects web applications from cross-site forgery, cross-site scripting (XSS), file inclusion, and SQL injection, among other things. A WAF is a protocol layer 7 (in the OSI model) protection that is not intended to protect against all forms of attacks. This method of attack mitigation is typically part of a suite of tools that, when combined, generate a comprehensive defence against a variety of attack vectors.
When a WAF is deployed in front of a web application, it creates a barrier between the web application and the Internet. While a proxy server protects the identity of a client computer by acting as an intermediary, a WAF is a form of reverse proxy that protects the server from disclosure by requiring clients to move through the WAF before reaching the server.
A WAF operates according to a set of laws known as policies. These policies aim to protect against device vulnerabilities by filtering out malicious traffic. The benefit of a WAF stems in part from the speed and ease with which policy modifications can be enforced, allowing for quicker response to varying attack vectors; for example, rate limiting can be easily implemented during a DDoS attack by changing WAF policies.
What is the difference between blocklist and allowlist WAFs?
A WAF that uses a blocklist (negative protection model) defends against known attacks. Consider a blocklist WAF to be a club bouncer who is told to refuse admission to guests who do not adhere to the dress code. A WAF based on an allow list (positive security model), on the other hand, only allows pre-approved traffic. This is analogous to the bouncer at a private party; he or she only accepts those who are on the list. Both blocklists and allowlists have advantages and disadvantages, which is why many WAFs have a hybrid security model that incorporates both.
What are network-based, host-based, and cloud-based WAFs?
A WAF can be applied in one of three ways, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages:
- In most cases, a network-based WAF is hardware-based. Since they are deployed locally, they reduce latency; however, network-based WAFs are the most costly choice and necessitate the storage and maintenance of physical equipment.
- A host-based WAF can be completely incorporated into the software of an application. This approach is less costly and more customizable than a network-based WAF. The disadvantages of a host-based WAF are the use of local server resources, the difficulty of deployment, and the cost of maintenance. These components usually necessitate engineering time and can be expensive.
- Cloud-based WAFs are a low-cost, easy-to-implement option; they typically include a turnkey installation that is as simple as a DNS change to redirect traffic. Cloud-based WAFs often have a low upfront cost because consumers pay for protection as a service on a monthly or annual basis. Cloud-based WAFs can also include a solution that is constantly updated to defend against the most recent threats with no additional work or expense on the user's part. The disadvantage of a cloud-based WAF is that users hand over responsibility to a third party, so certain functionality of the WAF might be opaque to them. Discover Cloudflare's cloud-based WAF solution.
If you think that your website is safe from any hacking attempts, think again! With a rise in hacking attacks, your website is vulnerable and there is a chance of your website getting compromised. Various website security measures are on the rise and they are for your website’s good.
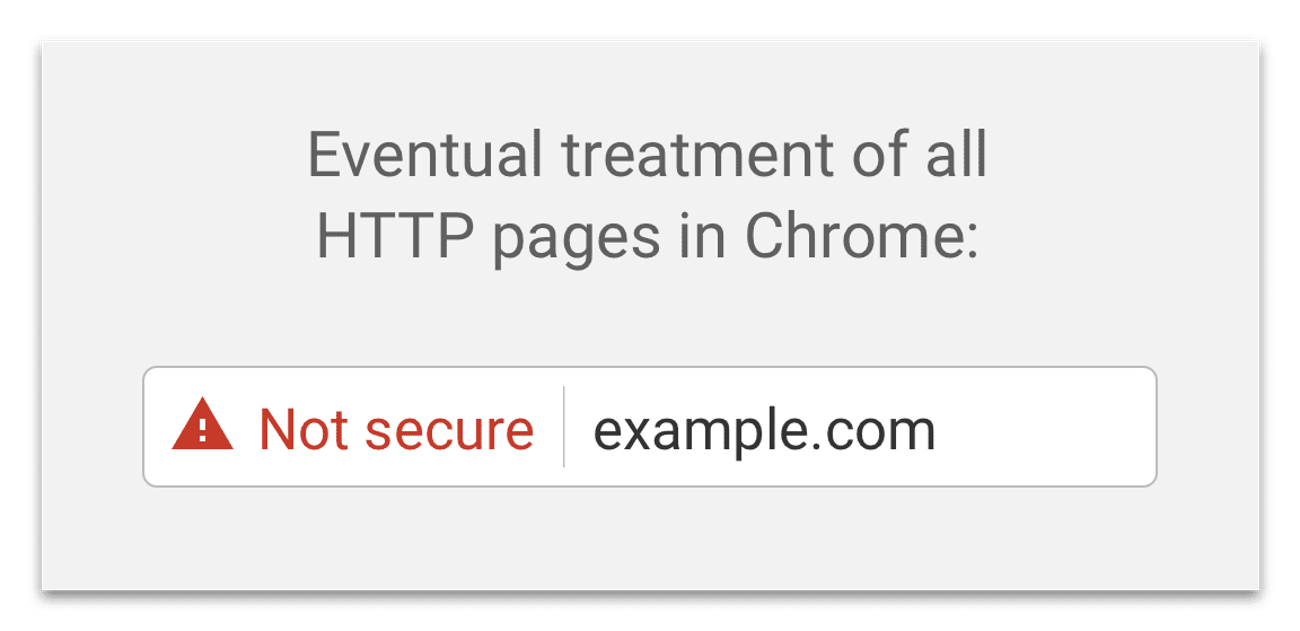
Google has also been emphasizing that every website should switch to HTTPS; this means that every website should have an SSL certificate installed on it. Google gives prime importance to websites with ‘HTTPS ‘ and not having an SSL certificate installed on your website might result in a decrease in your website’s search engine rankings and there are also chances of your website getting flagged in various browsers and thereby, it will be determined as not a safe website to browse. If a big red warning is displayed along with your website, your website viewers are not going to feel very confident and comfortable browsing your website or purchasing from your website.
Here is how Chrome displays a website that is not safe:
Having your website URL starting with ‘HTTPS’ is a great way to display the credibility of your website and it is also an important attribute for any website that collects customer information; this includes all the e-commerce websites and lead generation websites as well. If you have a form on your website that has to be filled by the customers or if you accept any kind of payments online, you must have an SSL certificate installed that denotes your website with HTTPS. This also holds true for every kind of business website out there.
Having HTTPS is not enough!
If you have HTTPS installed on your website, you can believe that your website security is absolutely secure! That, however, is not the case! HTTPS is an essential layer of website protection, but your website needs more. Website protection is a hot subject that many website owners and experts are debating right now. Every day, there is news of major website hacks. The majority of company and e-commerce store websites are vulnerable to identity fraud and Equifax breaches. Even if a large business website appears to be stable, this is not always the case. Even though an SSL certificate was present, the Equifax breach hack was carried out. The reality is that HTTPS will not always be able to prevent hackers from infiltrating your website's database. HTTPS cannot prevent malicious attacks that can bring your entire website down and steal all of your vital customer information; therefore, you need something else to protect your business website.
What you need is a web application firewall!
If your website already uses HTTPS, you have completed the most critical first step. If your website isn't even using HTTPS, you can start now! Having HTTPS on your website is the bare minimum of protection, and once you've done that, it's time to move on! To go the extra mile in terms of website protection, invest in a web application firewall. The web application firewall is made up of a series of rules that are intended to protect your website. They are as follows:
Preventing unnecessary web traffic from reaching your website
Defending the website from hacking attempts, brute force attacks, DDoS attacks, SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and zero-day exploits
Digital patching is done before the official patches are published by the famous CMS platforms.
Much of this is accomplished daily rather than on an as-needed basis, ensuring the full protection of your website. In other words, a web application firewall will detect and avoid an attack until it is successful. Also with all of this, if a hacker tries to access your website, a web application firewall (WAF) can assist you in cleaning your entire website faster and at a lower cost.
A web application firewall is more than that – Via advanced caching technology, a WAF also improves website speed and ensures efficient efficiency. After installing a web application firewall on your website, it becomes quicker and safer, which are two of the most significant characteristics in today's international web environment.
You may believe that your website is not a target for hackers and that you do not need a web application firewall!
You may believe that your website is secure, but the TRUTH is quite the opposite! Many website owners believe that hackers typically target large websites. After all, what good is it for a hacker to infiltrate a website that only receives a few visitors every month? The response is that a hacker can get a lot more out of your website than you expect. In today's world, most hackers not only go after big data, but they also try to steal people's social security numbers and credit card details in a single shot.
A wide variety of hacking attempts is made for relatively non-harmful reasons. For example, many hackers can infiltrate your webserver to send out a large number of spam emails. Hackers can inject malicious code into the website, affecting its performance and reliability.
A website hack may also result in the message – ‘This site could be compromised' in Google search results, which has a slew of negative consequences, including:
Loss or destruction of data
Decrease in customer confidence
Breach of sensitive information and customer information
Your website or emails getting blacklisted
Huge drops in your website’s search engine rankings
Lost business and lost revenue
In most cases, hackers do not intend to harm your company, but if your website is vulnerable, you will undoubtedly face the negative consequences mentioned above.
It is a fact that your website, no matter how large or small, is a target for hackers.
Conclusion
Your website is the idea that you have introduced, and it is vulnerable to being hacked; hence, it is important to protect it with all security measures. Since you have a website, you are a potential target for hackers. Having strong passwords for your website and installing an SSL certificate on your website is insufficient to fully secure your website. As critical as the internet is for generating a lot of business, it also has its own set of risks. So, to secure your website and ensure the best possible results, you must have a web application firewall. This is a small price to pay to protect your website from hacking attempts and, as a result, avoid incurring large costs in the long run.Haven’t tried a web application firewall yet? Fast Web Host provides you with a free trial of a WAF, check out for yourself what a WAF can do for your website – Get Website Hosting Free Trial